How To Add Extra Blog In Domain_9
You can set up or update certain DNS records and your repository settings to point the default domain for your GitHub Pages site to a custom domain.
GitHub Pages is available in public repositories with GitHub Free and GitHub Free for organizations, and in public and private repositories with GitHub Pro, GitHub Team, GitHub Enterprise Cloud, and GitHub Enterprise Server. For more information, see "GitHub's products."
People with admin permissions for a repository can configure a custom domain for a GitHub Pages site.
About custom domain configuration
Make sure you add your custom domain to your GitHub Pages site before configuring your custom domain with your DNS provider. Configuring your custom domain with your DNS provider without adding your custom domain to GitHub could result in someone else being able to host a site on one of your subdomains.
The dig command, which can be used to verify correct configuration of DNS records, is not included in Windows. Before you can verify that your DNS records are configured correctly, you must install BIND.
Note: DNS changes can take up to 24 hours to propagate.
Configuring a subdomain
To set up a www or custom subdomain, such as www.example.com or blog.example.com, you must add your domain in the repository settings, which will create a CNAME file in your site's repository. After that, configure a CNAME record with your DNS provider.
-
On GitHub, navigate to your site's repository.
-
Under your repository name, click Settings.

-
In the left sidebar, click Pages.

-
Under "Custom domain", type your custom domain, then click Save. This will create a commit that adds a CNAME file in the root of your publishing source.

-
Navigate to your DNS provider and create a
CNAMErecord that points your subdomain to the default domain for your site. For example, if you want to use the subdomainwww.example.comfor your user site, create aCNAMErecord that pointswww.example.comto<user>.github.io. If you want to use the subdomainwww.anotherexample.comfor your organization site, create aCNAMErecord that pointswww.anotherexample.comto<organization>.github.io. TheCNAMErecord should always point to<user>.github.ioor<organization>.github.io, excluding the repository name. For more information about how to create the correct record, see your DNS provider's documentation. For more information about the default domain for your site, see "About GitHub Pages."Warning: We strongly recommend not using wildcard DNS records, such as
*.example.com. A wildcard DNS record will allow anyone to host a GitHub Pages site at one of your subdomains. -
Open Terminal Terminal Git Bash.
-
To confirm that your DNS record configured correctly, use the
digcommand, replacing WWW.EXAMPLE.COM with your subdomain.$ dig WWW.EXAMPLE.COM +nostats +nocomments +nocmd > ;WWW.EXAMPLE.COM. IN A > WWW.EXAMPLE.COM. 3592 IN CNAME YOUR-USERNAME.github.io. > YOUR-USERNAME.github.io. 43192 IN CNAME GITHUB-PAGES-SERVER . > GITHUB-PAGES-SERVER . 22 IN A 192.0.2.1 -
If you use a static site generator to build your site locally and push the generated files to GitHub, pull the commit that added the CNAME file to your local repository. For more information, see "Troubleshooting custom domains and GitHub Pages."
-
Optionally, to enforce HTTPS encryption for your site, select Enforce HTTPS. It can take up to 24 hours before this option is available. For more information, see "Securing your GitHub Pages site with HTTPS."

Configuring an apex domain
To set up an apex domain, such as example.com, you must configure a CNAME file in your GitHub Pages repository and at least one ALIAS, ANAME, or A record with your DNS provider.
If you are using an apex domain as your custom domain, we recommend also setting up a www subdomain. If you configure the correct records for each domain type through your DNS provider, GitHub Pages will automatically create redirects between the domains. For example, if you configure www.example.com as the custom domain for your site, and you have GitHub Pages DNS records set up for the apex and www domains, then example.com will redirect to www.example.com. Note that automatic redirects only apply to the www subdomain. Automatic redirects do not apply to any other subdomains, such as blog. For more information, see "Configuring a subdomain."
-
On GitHub, navigate to your site's repository.
-
Under your repository name, click Settings.

-
In the left sidebar, click Pages.

-
Under "Custom domain", type your custom domain, then click Save. This will create a commit that adds a CNAME file in the root of your publishing source.

-
Navigate to your DNS provider and create either an
ALIAS,ANAME, orArecord. You can also createAAAArecords for IPv6 support. For more information about how to create the correct record, see your DNS provider's documentation.- To create an
ALIASorANAMErecord, point your apex domain to the default domain for your site. For more information about the default domain for your site, see "About GitHub Pages." - To create
Arecords, point your apex domain to the IP addresses for GitHub Pages.185.199.108.153 185.199.109.153 185.199.110.153 185.199.111.153 - To create
AAAArecords, point your apex domain to the IP addresses for GitHub Pages.2606:50c0:8000::153 2606:50c0:8001::153 2606:50c0:8002::153 2606:50c0:8003::153
Warning: We strongly recommend not using wildcard DNS records, such as
*.example.com. A wildcard DNS record will allow anyone to host a GitHub Pages site at one of your subdomains. - To create an
-
Open Terminal Terminal Git Bash.
-
To confirm that your DNS record configured correctly, use the
digcommand, replacing EXAMPLE.COM with your apex domain. Confirm that the results match the IP addresses for GitHub Pages above.- For
Arecords.$ dig EXAMPLE.COM +noall +answer -t A > EXAMPLE.COM 3600 IN A 185.199.108.153 > EXAMPLE.COM 3600 IN A 185.199.109.153 > EXAMPLE.COM 3600 IN A 185.199.110.153 > EXAMPLE.COM 3600 IN A 185.199.111.153 - For
AAAArecords.$ dig EXAMPLE.COM +noall +answer -t AAAA > EXAMPLE.COM 3600 IN AAAA 2606:50c0:8000::153 > EXAMPLE.COM 3600 IN AAAA 2606:50c0:8001::153 > EXAMPLE.COM 3600 IN AAAA 2606:50c0:8002::153 > EXAMPLE.COM 3600 IN AAAA 2606:50c0:8003::153
- For
-
If you use a static site generator to build your site locally and push the generated files to GitHub, pull the commit that added the CNAME file to your local repository. For more information, see "Troubleshooting custom domains and GitHub Pages."
-
Optionally, to enforce HTTPS encryption for your site, select Enforce HTTPS. It can take up to 24 hours before this option is available. For more information, see "Securing your GitHub Pages site with HTTPS."

Configuring an apex domain and the www subdomain variant
When using an apex domain, we recommend configuring your GitHub Pages site to host content at both the apex domain and that domain's www subdomain variant.
To set up a www subdomain alongside the apex domain, you must first configure an apex domain, which will create an ALIAS, ANAME, or A record with your DNS provider. For more information, see "Configuring an apex domain."
After you configure the apex domain, you must configure a CNAME record with your DNS provider.
- Navigate to your DNS provider and create a
CNAMErecord that pointswww.example.comto the default domain for your site:<user>.github.ioor<organization>.github.io. Do not include the repository name. For more information about how to create the correct record, see your DNS provider's documentation. For more information about the default domain for your site, see "About GitHub Pages." - To confirm that your DNS record configured correctly, use the
digcommand, replacing WWW.EXAMPLE.COM with yourwwwsubdomain variant.$ dig WWW.EXAMPLE.COM +nostats +nocomments +nocmd > ;WWW.EXAMPLE.COM. IN A > WWW.EXAMPLE.COM. 3592 IN CNAME YOUR-USERNAME.github.io. > YOUR-USERNAME.github.io. 43192 IN CNAME GITHUB-PAGES-SERVER . > GITHUB-PAGES-SERVER . 22 IN A 192.0.2.1
Removing a custom domain
-
On GitHub, navigate to your site's repository.
-
Under your repository name, click Settings.

-
In the left sidebar, click Pages.

-
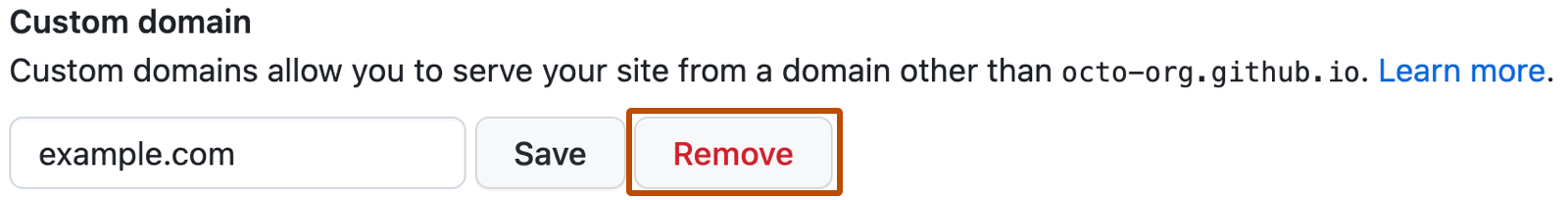
Under "Custom domain," click Remove.
Securing your custom domain
If your GitHub Pages site is disabled but has a custom domain set up, it is at risk of a domain takeover. Having a custom domain configured with your DNS provider while your site is disabled could result in someone else hosting a site on one of your subdomains.
Verifying your custom domain prevents other GitHub users from using your domain with their repositories. If your domain is not verified, and your GitHub Pages site is disabled, you should immediately update or remove your DNS records with your DNS provider. For more information, see "Verifying your custom domain for GitHub Pages."
Further reading
- "Troubleshooting custom domains and GitHub Pages"
How To Add Extra Blog In Domain_9
Source: https://docs.github.com/en/pages/configuring-a-custom-domain-for-your-github-pages-site/managing-a-custom-domain-for-your-github-pages-site
Posted by: crewsmistne.blogspot.com

0 Response to "How To Add Extra Blog In Domain_9"
Post a Comment